Queue.
•Define queue.
ANS.: Collection of elements using FIFO (First in First Out) mechanism.
•Operations performed on queue?
ANS.: enqueue (insertion), dequeue (deletion) & display.
•. Applications of queue?
ANS.: Round Robin technique for processor scheduling, Customer services application, Printer server routines.
•Types of queue?
ANS.: Linear queue, circular queue, double ended queue, priority queue.
Program for Queue using linked list.
Graphically Representation.
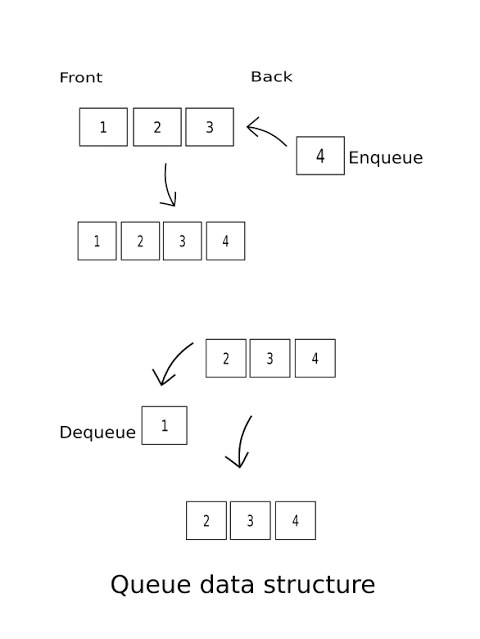
Source code.
//queue using linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node * addr;
};
struct node * head ,* rear;
void ins(int);
void del();
void disp();
int main()
{
ins(10);\\ insert 10
ins(20);\\ insert 10 20
ins(30);\\ insert 10 20 30
ins(40);\\ insert 10 20 30 40
del();\\ delete 10(20 30 40)
del();\\ delete 20(30 40)
del();\\ delete 30(40)
}
void ins(int val)
{
struct node * temp,*i=head;
temp=(struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
temp -> data=val;
temp-> addr=NULL;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=temp;
rear=temp;
}
else
rear->addr=temp;
rear=temp;
disp();
}
void disp()
{
struct node * i=head;
printf("\nqueue : ");
while(i!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ",i->data);
i=i->addr;
}
}
void del()
{
//if queue is empty
if(head==NULL)
printf("Error:empty\n");
//else
else
{
//more than one node exist
head=head->addr;
//only one node exist
if(head==NULL)
rear=NULL;
}
//display
disp();
}Output.
queue : 10
queue : 10 20
queue : 10 20 30
queue : 10 20 30 40
queue : 20 30 40
queue : 30 40
queue : 40

